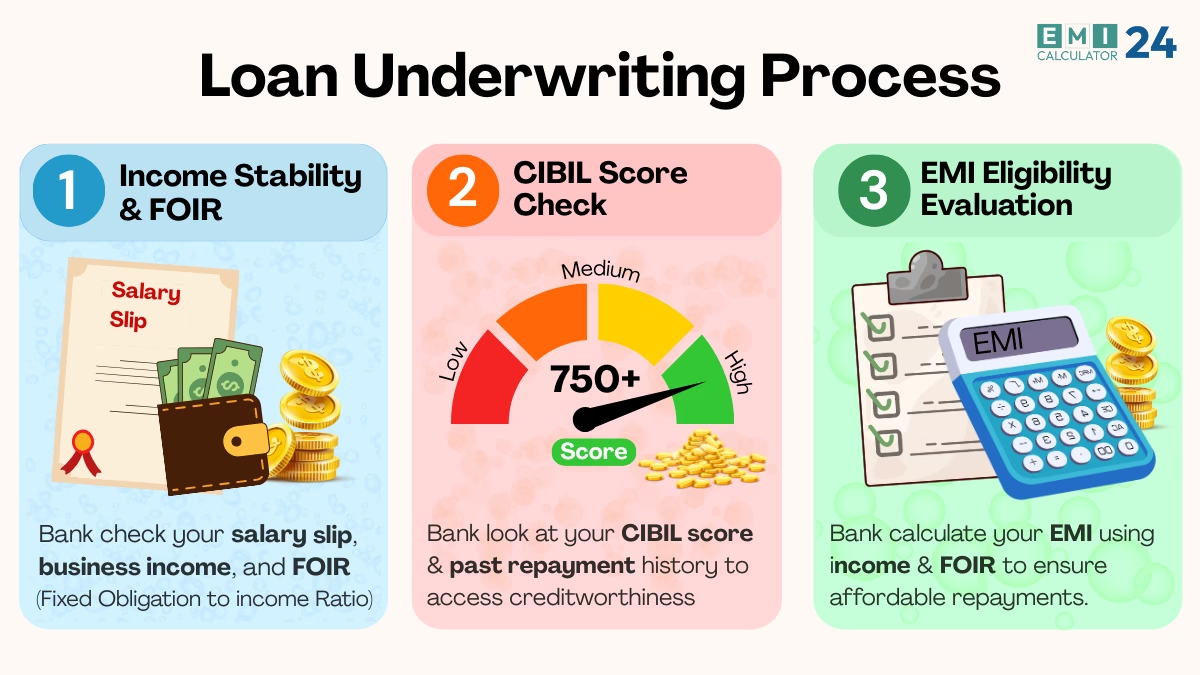
The Loan Underwriting Process is a critical step in bank loan approval. Understanding how banks assess your income, CIBIL score, and EMI eligibility can significantly improve your chances of getting a loan approved. 💰🏦
In this guide, we explain everything step by step, with practical examples for salaried and self-employed borrowers. 💰📊
| Calculate Your EMI Now |
What Is Loan Underwriting? A Simple Explanation for Borrowers
Meaning of loan underwriting in simple terms 📝
Loan underwriting is like a financial safety check. Banks analyze whether you can repay the loan without risk. Think of it as a step before the loan sanction, ensuring your financial profile meets the bank’s risk criteria. ✅
Why banks use underwriting before approving loans
-
Mitigate default risk ⚠️
-
Ensure EMI affordability 💸
-
Follow regulatory norms in India 🇮🇳
Difference between loan underwriting and loan sanction
| Aspect | Loan Underwriting | Loan Sanction |
|---|---|---|
| Purpose | Risk assessment ⚖️ | Official approval and issuing sanction letter 🏦 |
| Timing | Before sanction ⏳ | After underwriting approval ✅ |
| Outcome | Approval/rejection/modification ❌ | Loan sanction letter issued; funds ready for disbursement 💰 |
Who performs underwriting in banks (automated vs manual)
-
Automated 🤖: Software checks CIBIL, income, FOIR, EMIs, and past loan history instantly.
-
Manual 👨💼: Underwriters review documents, employment proof, and bank statements for accuracy.
How the Loan Underwriting Process Works in Banks (Step-by-Step)
Loan application submission and initial screening 📝
The bank collects your personal and financial information to begin preliminary checks.
Document verification and data validation 🔍
Bank verifies ID, income proofs, property documents (for home loans), and KYC documents.
Credit risk assessment by the bank 📊
CIBIL score and past credit history are analyzed to determine repayment reliability.
Income and repayment capacity evaluation 💼
Banks calculate EMI eligibility using your income and FOIR.
Final underwriting outcome ✅
-
Approved 👍: Loan can proceed to sanction.
-
Modified ✏️: Bank may adjust loan amount or tenure.
-
Rejected ❌: High-risk or insufficient financial capacity.
Role of EMI in the Loan Underwriting Process
How banks decide affordable EMI limits 💸
Banks typically permit salaried borrowers to commit up to 50–60% of their monthly earnings to loan repayments. For business owners, banks consider cash flow and stability before setting EMI limits.
Income vs EMI ratio and its importance 📐
Formula: To calculate the percentage of income spent on EMIs: (EMI ÷ Monthly Income) × 100.
Example: ₹25,000 EMI ÷ ₹70,000 income × 100 = 35.7% → safe EMI limit ✅
This ensures your EMIs do not exceed your repayment capacity.
| Check Your EMI Eligibility |
Impact of existing EMIs on new loan approval 📊
If you already have loans, banks calculate the total EMI burden. For example, if your FOIR exceeds 50%, your new loan may be reduced or rejected.
Effect of tenure and interest rate on EMI eligibility ⏳💰
-
Longer tenure → Lower EMI, higher total interest
-
Shorter tenure → Higher EMI, lower total interest
Balancing tenure and EMIs helps maximize loan eligibility without financial stress.
Role of CIBIL Score in Bank Loan Approval
How CIBIL score is used in underwriting decisions 📈
Banks weigh CIBIL score along with income and FOIR to assess risk. A higher CIBIL score signals reliable repayment history, which can increase your approved loan amount and reduce interest rates.
Safe CIBIL score range for loan approval in India 🇮🇳
-
750+ → Excellent 🌟
-
700–749 → Good 👍
-
650–699 → Moderate ⚠️ (may require higher down payment or co-applicant)
Impact of poor credit history on approval chances 📉
Low CIBIL scores or missed EMIs may lead to:
-
Loan rejection ❌
-
Lower loan amounts 💸
-
Higher interest rates 💰
No Credit History vs. Bad Credit History: Key Distinctions
-
No credit history 🤔: Banks may cautiously approve, often with a co-applicant or collateral.
-
Bad credit history ⚠️: Bank may reject or approve only at higher rates.
Role of Income and FOIR in Loan Underwriting Decisions
How banks evaluate income stability 💼
-
Salaried: Consistent 6–12 months salary or bonuses 💰
-
Business: 2–3 years of profitable operations 📊
Salary vs business income assessment 💹
-
Salary: Predictable, easier EMI calculation ✅
-
Business: Bank evaluates profit, cash flow, and sustainability 📈
FOIR (Fixed Obligation to Income Ratio) explained 📐
Formula: Total EMIs ÷ Net Monthly Income × 100
Maximum FOIR: The highest FOIR for salaried borrowers is around 50%, with self-employed applicants often allowed a bit less.
How FOIR affects EMI limits and loan amount 💸
Higher FOIR → Lower loan amount, even with high income. Banks avoid overburdening borrowers financially.
Example:
Income = ₹80,000/month, Existing EMIs = ₹20,000
Proposed EMI: ₹20,000 → FOIR calculation: (20,000 + 20,000) divided by 80,000, multiplied by 100, resulting in 50% ✅
Loan may be approved but not increased beyond this EMI limit.
Other Important Factors Checked During the Loan Underwriting Process
-
Applicant age and remaining earning years ⏳
-
Loan amount vs repayment capacity 💸
-
Employment type and employer profile 👔
-
Type of loan and associated risk level 🏡🚗
-
Bank-specific underwriting policies 🏦
Common Reasons Why Banks Reject Loans After Underwriting
-
EMI burden higher than bank limits ❌
-
Weak or inconsistent credit profile 📉
-
Unstable income or employment history 🔄
-
Document mismatch or verification issues 📄
-
Borrower profile outside bank risk policy ⚠️
How an EMI Calculator Helps You Prepare for Loan Underwriting
-
Estimate affordable EMI before applying 📱
-
Understand loan amount vs tenure impact 📈
-
Avoid over-borrowing mistakes ⚠️
-
Reduce chances of loan rejection ✅
Tips to Improve Your Loan Underwriting Approval Chances
-
Improve and maintain CIBIL score 📈
-
Reduce existing EMIs and liabilities 💸
-
Choose realistic loan amount and tenure 🏠
-
Keep documents accurate and updated 📄
FAQs on Loan Underwriting and Bank Loan Approval
Q1: What is the loan underwriting process in banks?
A1: The Loan Underwriting Process is the method banks use to assess the risk of lending you money. It involves verifying your documents, evaluating credit history, checking income stability, and calculating EMI affordability before approving a loan. ✅
Q2: How long does loan underwriting usually take?
A2: Typically, underwriting takes 3–10 business days for personal and home loans. Business or complex loans may take longer due to detailed financial checks. ⏳
Q3: Can a loan be rejected after underwriting approval?
A3: Yes, even after initial underwriting approval, loans can be rejected if documents mismatch, credit behavior changes, or the bank revises its risk policy. ⚠️
Q4: Does EMI calculation affect loan underwriting?
A4: Absolutely! Banks use EMI eligibility calculations to ensure your monthly payments don’t exceed your income capacity. High existing EMIs can reduce the loan amount approved.
Q5: Is underwriting same for all types of loans?
A5: No. While the Loan Underwriting Process is similar, home loans, personal loans, business loans, and vehicle loans have different risk evaluation parameters. 🏡🚗💼
Final Thoughts on the Loan Underwriting Process
The Loan Underwriting Process ensures banks lend responsibly while protecting borrowers from over-commitment. By managing your EMI, maintaining a healthy CIBIL score, and demonstrating stable income, you can improve your approval chances. Smart financial planning and understanding the underwriting steps make you a confident borrower. 💪💡
Real-life Example:
Rajesh earns ₹80,000/month and wants a home loan. His existing EMIs = ₹20,000. Bank calculates FOIR = (20,000 + proposed EMI)/80,000 = 50% max limit ✅. With stable income and CIBIL 780, his loan gets approved. 🏠💰